What Is Automated Test Equipment?
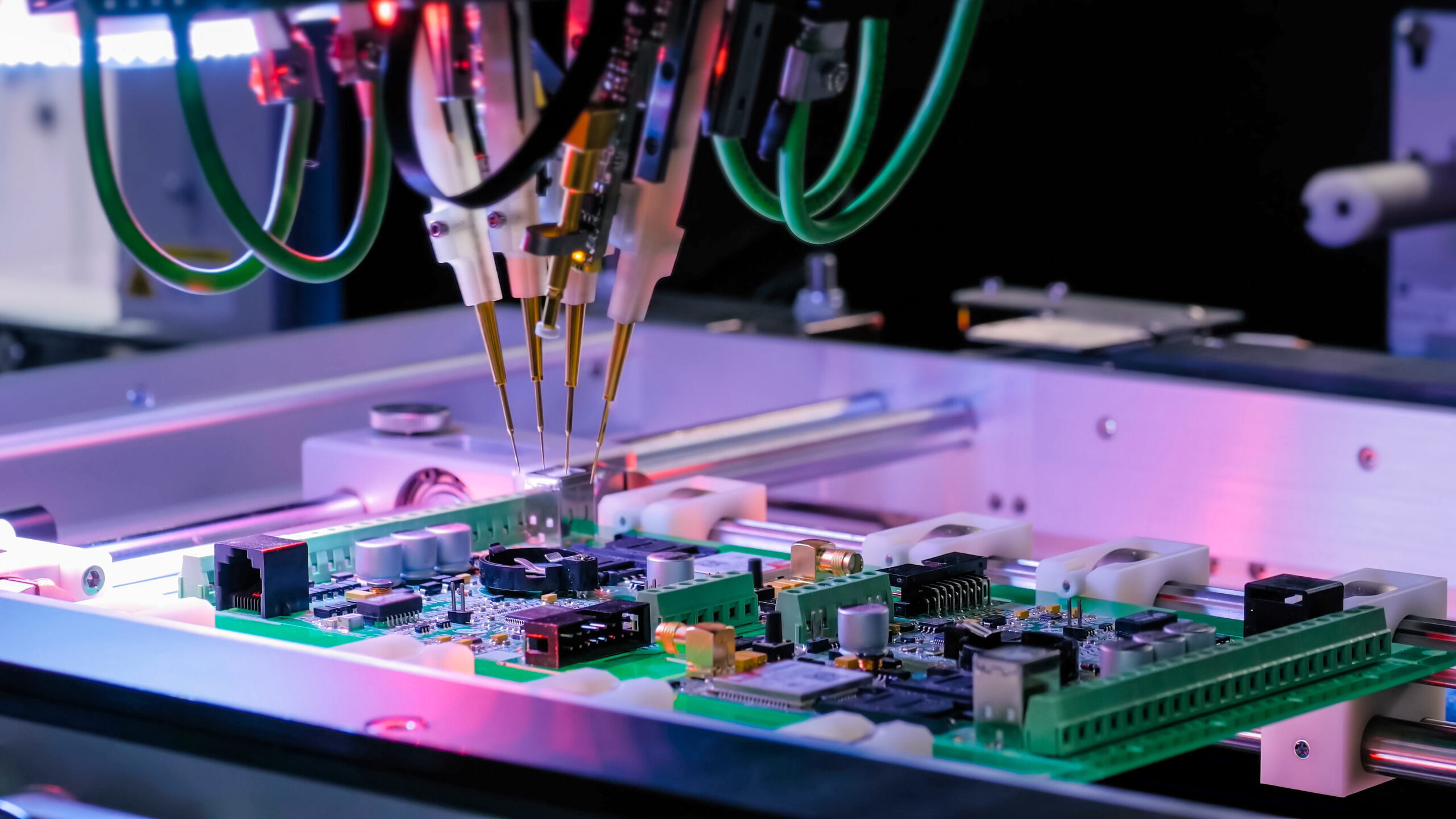
Do you find the challenge of electronics functional tests within a tight production schedule overwhelming? We've been in your shoes, felt the pressure, and recognized the relief that Automated Test Equipment (ATE) can bring.
This groundbreaking automation technology is extensively employed in industries such as semiconductors and electronics to ensure swift and precise testing of devices.
Join us as we delve into what ATE is, how it operates, its advantages, and why it might be your solution for streamlining manufacturing processes. So let's begin simplifying complex testing scenarios!
Understanding Automated Test Equipment (ATE)
Automated Test Equipment (ATE) represents an advanced type of computerized machinery explicitly designed for electronics functional tests that check the operational capabilities of various electronic components and systems. ATE employs specialized test instruments to measure and analyze results.
True to its name, this technological tool primarily ensures the reliability and quality of these components through electronics functional testing while minimizing the need for human intervention. By utilizing automated testing procedures, potential human errors are reduced, and a single ATE system can efficiently perform individual or sequential tests on multiple devices simultaneously.
This technology finds widespread application across various industries, including semiconductor manufacturing, electronics, aerospace, and automotive production. Its primary role is identifying defects early in manufacturing and validating that products meet specified standards or requirements.
Transitioning from manual to automated testing tools has brought about a revolutionary change for sectors heavily reliant on detecting faults and conducting electronics functional tests to assure product quality. This shift provides an effective means of maintaining rigorous quality control measures throughout all stages of production.
Components of an ATE System
An Automated Test Equipment (ATE) system comprises a combination of various components working together to carry out thorough testing operations. Here, we outline the essential components that ensure ATE systems function effectively.
- Test Instruments: These instruments have a primary role in generating and measuring electrical signals necessary for testing the functionality and performance of devices under test (DUT). They also aid in capturing valuable test data.
- Instrument Controllers: Responsible for supervising operations and managing communication with the test instruments, instrument controllers ensure smooth interaction among different hardware components.
- Test Fixtures: Acting as mechanical structures, test fixtures secure DUTs in place and establish vital electrical connections for testing. They enable ATE systems to conduct tests on single or multiple devices concurrently.
- Software Components: An integral part of an ATE system, software elements encompass test programs, drivers, and user interfaces that govern the testing process from beginning to end and analyze the resulting test data. This involves employing automatic test pattern generation (ATPG) to transmit precise test patterns to the DUT for effective testing.
- Electronic Devices: The electronic equipment within an ATE system encompasses a wide spectrum, ranging from simple components like diodes and resistors to intricate integrated circuits in aerospace or wireless communication applications.
Applications and Industries That Use ATE
Automated Test Equipment (ATE) has become crucial across multiple industries, contributing significantly to their development and innovation. It's extensively utilized in wireless communication and radar systems due to its unparalleled capability to test printed circuit boards, ensure seamless interconnections, and conduct effective electronics functional tests and verifications.
Industries such as defense and aerospace also frequently rely on ATE for data acquisition and as an indispensable diagnostic tool. A striking increase is projected within the ATE market in consumer electronics and automotive industries. This can be attributed to the burgeoning demand for more efficient, faster stress-testing methods with minimal human interaction.
Additionally, semiconductors, often fundamental components of electronic devices today, undergo rigorous electronics functional testing facilitated by advanced ATE systems before being integrated into various products.
Increased Testing Efficiency and Accuracy
Automated Test Equipment (ATE) offers a significant advantage in increasing testing efficiency and accuracy. With ATE, the testing process becomes automated, eliminating manual errors and reducing the need for human intervention.
This results in consistent and precise testing results, ensuring that each test is performed with the same level of accuracy every time. Additionally, ATE allows faster testing than manual methods, enabling companies to conduct more frequent tests within a shorter time frame.
The streamlined nature of ATE also enhances resource utilization, making the overall testing process more efficient and cost-effective. Moreover, real-time reporting capabilities provide instant feedback on test results, allowing for prompt analysis and decision-making.
Cost Savings and Time Optimization
Using Automated Test Equipment (ATE) can lead to significant cost savings and time optimization. By automating the testing process, companies can reduce test and cycle times, increasing efficiency in product development and manufacturing units.
The automation factor of ATE minimizes the need for human intervention in manual testing, accelerating the overall testing timeline. This saves valuable time and reduces labor costs associated with manual testing processes.
Additionally, ATE offers repeatability of the verification procedure, ensuring consistent and reliable results every time a test is conducted. With high volumes of devices or equipment to be tested, ATE provides cost-effective solutions, eliminating the need for extensive manpower resources.
Improved Quality Control
Using Automated Test Equipment (ATE) offers a significant advantage in improving quality control. ATE provides precision and accuracy in testing, ensuring that products meet the desired quality standards.
By automating the testing process, ATE reduces the potential for human error and ensures consistent and reliable results. This is particularly important in industries such as aerospace and semiconductor, where product integrity and reliability are critical.
Implementing ATE helps identify defects or issues earlier in the production cycle, allowing for prompt corrective action. With improved quality control through ATE, businesses can deliver higher-quality products to their customers while reducing costs associated with fixing post-release glitches or failures.
How Automated Testing Works
Automated testing works through a process of test automation using specialized tools and software to carry out various types of tests on electronic devices. These tests include functional testing, measurement testing, and more.
Continue reading to learn more about the different methods and tools used in automated testing and the data analysis and reporting involved.
Test Automation Process and Tools
Automated testing streamlines the software testing process through various steps and specialized tools:
- Creating Scripted Interactions: In automated testing, scripted sequences of actions are developed and executed using testing tools. These scripts emulate user interactions, ensuring comprehensive testing.
- Utilizing Testing Tools: Specific tools for automation testing are employed. They analyze the software, generate reports, and compare outcomes against expected behavior. These tools are essential for accurate testing and reporting.
- Thorough Software Analysis: Automated testing tools meticulously scrutinize the software. They identify bugs, errors, and other issues by conducting diverse checks across different software aspects, guaranteeing reliability and functionality.
- Detailed Outcome Reports: These tools comprehensively report each test case's outcomes after executing automated tests. These reports offer insights into failures or errors during the testing phase.
- Comparing Actual vs. Expected Behavior: Automation testing involves contrasting accurate results with anticipated behavior outlined in test cases. By juxtaposing these two sets of data, discrepancies are pinpointed, facilitating necessary adjustments.
- Dedicated Testing Software: Specialized software tailored for automated testing is pivotal. These tools encompass features like record-playback functionality, test case management, and result analysis, enhancing the testing process.
- Automated Test Case Execution: Automation testing tools autonomously execute predefined test cases, eliminating the need for manual intervention. This approach is a time-efficient alternative to manual testing methodologies.
Test Types and Methods
Automated testing streamlines the software testing process through various steps and specialized tools:
- Creating Scripted Interactions: In automated testing, scripted sequences of actions are developed and executed using testing tools. These scripts emulate user interactions, ensuring comprehensive testing.
- Utilizing Testing Tools: Specific tools for automation testing are employed. They analyze the software, generate reports, and compare outcomes against expected behavior. These tools are essential for accurate testing and reporting.
- Thorough Software Analysis: Automated testing tools meticulously scrutinize the software. They identify bugs, errors, and other issues by conducting diverse checks across different software aspects, guaranteeing reliability and functionality.
- Detailed Outcome Reports: These tools comprehensively report each test case's outcomes after executing automated tests. These reports offer insights into failures or errors during the testing phase.
- Comparing Actual vs. Expected Behavior: Automation testing involves contrasting accurate results with anticipated behavior outlined in test cases. By juxtaposing these two sets of data, discrepancies are pinpointed, facilitating necessary adjustments.
- Dedicated Testing Software: Specialized software tailored for automated testing is pivotal. These tools encompass features like record-playback functionality, test case management, and result analysis, enhancing the testing process.
- Automated Test Case Execution: Automation testing tools autonomously execute predefined test cases, eliminating the need for manual intervention. This approach is a time-efficient alternative to manual testing methodologies.
Data Analysis and Reporting
In automated testing, data analysis and reporting play a crucial role in understanding test results and improving the quality of the software being tested. Test automation tools generate detailed reports that analyze parameters such as test case execution, test results, and quality improvement metrics.
These reports provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the automated testing process and help identify any issues or areas for improvement. By analyzing the data collected during automated testing, teams can better understand how their software is performing under different conditions.
They can identify patterns or trends indicating potential problems or areas for further optimization. Additionally, these reports can track progress over time, compare results between different software versions, and make informed decisions about future development efforts.
With accurate and reliable data analysis and reporting, teams can ensure that their automated testing efforts are efficient and effective. They can quickly identify defects or performance issues in their software early in the development cycle, allowing for prompt resolution before they impact end users.
Conclusion
To wrap up, Automated Test Equipment (ATE) is a computerized system for conducting and assessing device tests. It brings forth many advantages, including heightened testing efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced quality control.
ATE assumes a pivotal role in vital sectors such as semiconductors, electronics, and PCB testing. It automates the testing procedures and guarantees precise outcomes. By proficiently managing time and resources without compromising accuracy, ATE persists in reshaping the landscape of testing equipment.
Author Bio
Daniel Jackson
Community Manager, NI
Daniel is a community manager for NI (formerly National Instruments), where they create the tools needed for companies to Engineer Ambitiously™. His current interests are at the intersection of software engineering and DevOps. Outside of work, he is a marathon runner and is working on his first novel.




